forge-db: SIMD-Accelerated Vector Search
High-performance vector database with IVF-PQ and HNSW indexing. Pure Rust, no external dependencies.
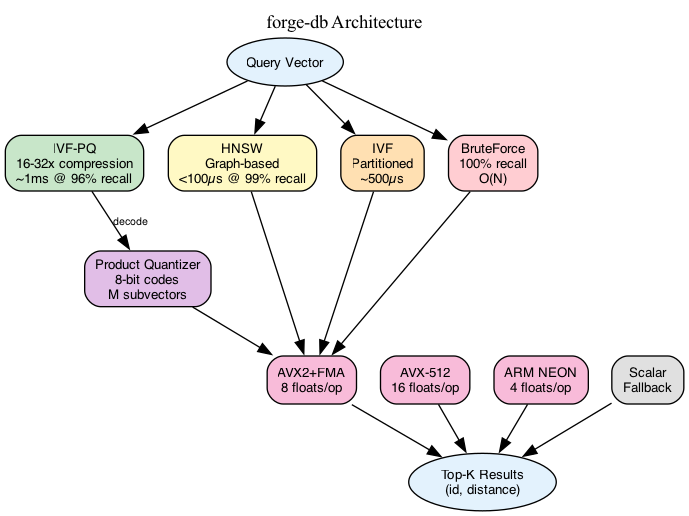
What It Does
Vector search finds the most similar items in a dataset. You have a query embedding (from an LLM, image encoder, etc.) and want the k nearest neighbors from millions of stored vectors. Brute force computes every distance—accurate but O(N). forge-db uses approximate algorithms that trade small recall losses for orders-of-magnitude speedups.
Use cases: semantic search, RAG retrieval, recommendation systems, duplicate detection. Anywhere you’d compute cosine similarity or L2 distance at scale.
Index Types
BruteForce: Computes all distances. 100% recall, O(N) time. Baseline for correctness testing and small datasets.
IVF (Inverted File): Partitions vectors into clusters via k-means. At query time, only search the nearest clusters. nprobe controls how many clusters to check—higher means better recall, slower search.
IVF-PQ: Adds Product Quantization to IVF. Vectors are compressed to 8-bit codes, reducing memory 16-32x. Distance computation uses precomputed lookup tables. The recall hit is ~5-10% but memory savings are massive.
HNSW: Hierarchical Navigable Small World graphs. Builds a multi-layer graph where each node connects to nearby vectors. Search is logarithmic—start at top layer, greedily descend. Best latency, highest memory usage.
SIMD Implementation
Distance computation dominates runtime. A 768-dim vector needs 768 multiplies and adds per comparison. SIMD processes multiple floats per instruction.
The implementation detects CPU features at startup:
- AVX-512: 16 floats/instruction
- AVX2+FMA: 8 floats/instruction
- ARM NEON: 4 floats/instruction
- Scalar fallback
Runtime dispatch means one binary runs optimally everywhere. No compile-time feature flags needed.
Product Quantization
PQ splits each vector into M subvectors (typically 8-32). Each subvector is quantized to the nearest centroid from a trained codebook. A 768-dim float32 vector (3KB) becomes 32 bytes.
At query time, compute distances from the query to all centroids once. Then for each database vector, sum the precomputed distances for its codes. This replaces 768 FMAs with 32 table lookups.
There tradeoff though, quantization introduces error. Reranking (fetch top-100 compressed, recompute exact distances, return top-10) recovers most recall.
Challenges & Lessons
This has probably been my most challenging rust project I have taken on. Cache alignment matters more than I expected. Aligning vectors to 64-byte boundaries improved throughput 15%. False sharing in parallel builds was another 10%.
Testing approximate algorithms is hard. “96% recall” means 4% of results are wrong. I built a test harness that compares against brute force and flags regressions. Statistical tests catch recall drops early.
Benchmarks
| Config | Latency | Recall | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|
| IVF-PQ nprobe=16 | 520µs | 69% | 31 MB |
| IVF-PQ + rerank | 1.0ms | 96% | 31 MB |
What I’d Do Differently
GPU acceleration is the obvious next step. Distance computation is insanely parallel. A CUDA backend would unlock another 10-100x.
I’d also explore binary quantization. 1-bit codes with Hamming distance are even faster than PQ for initial candidate filtering. This will be a good next step for my learning.